The process of evaluating, buying, and receiving green raw coffee involves several steps, from assessing coffee samples to finalizing the purchase and receiving the beans. Here’s an overview of the process:
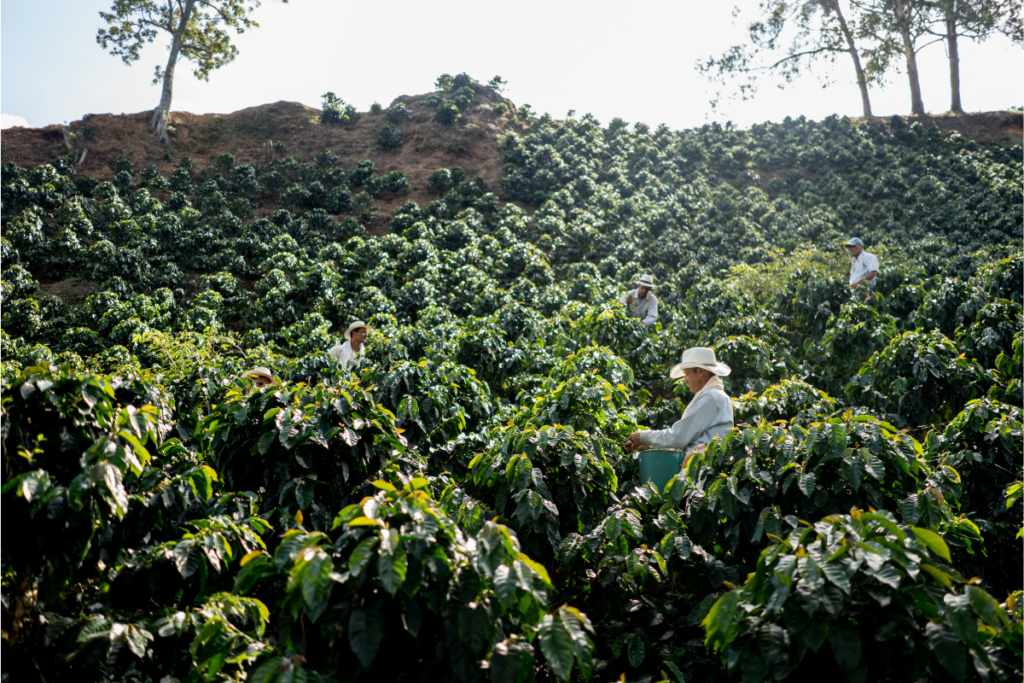
- Coffee Sample Evaluation:
- Coffee buyers typically receive samples of green coffee beans from potential suppliers or producers. These samples represent specific lots or batches of coffee beans and allow buyers to assess the quality, flavor profile, and suitability of the beans for their needs.
- Buyers conduct cupping sessions to evaluate the samples, following standardized protocols to assess aroma, flavor, acidity, body, and aftertaste. Cupping sessions involve brewing and tasting multiple samples side by side to compare and contrast their characteristics.
- Based on the results of the cupping sessions, buyers score and rank the samples, identifying preferred lots or batches of coffee beans that meet their quality standards and flavor preferences.
- Price Negotiation and Contracting:
- Once the preferred samples have been identified, buyers enter into negotiations with suppliers or producers to finalize the terms of the purchase. This includes negotiating prices, volumes, delivery schedules, and payment terms.
- Buyers may negotiate price premiums for high-quality or specialty-grade coffee beans, taking into account factors such as origin, processing method, and market demand.
- Once the terms are agreed upon, buyers and suppliers formalize the agreement through written contracts or purchase orders, specifying the details of the transaction and outlining the rights and obligations of both parties.
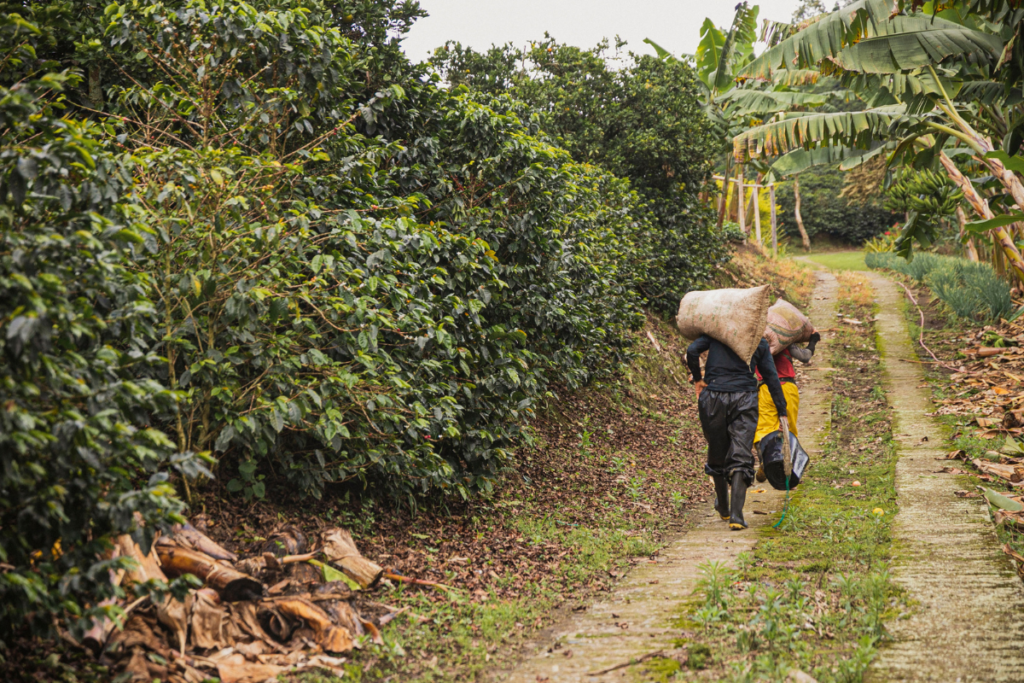
- Shipping and Logistics:
- After the purchase agreement is finalized, buyers coordinate shipping and logistics arrangements to transport the green coffee beans from the origin country to the destination. This involves selecting shipping methods, arranging transportation, and managing import/export documentation and customs clearance.
- Buyers may work with freight forwarders, logistics providers, and shipping agents to ensure smooth and timely delivery of the coffee beans. They also monitor shipping schedules and track the progress of shipments to anticipate any delays or issues that may arise during transit.
- Quality Control and Inspection:
- Upon arrival at the destination, the green coffee beans undergo quality control and inspection to verify their condition and quality. Buyers inspect the beans for any signs of damage, contamination, or defects that may have occurred during shipping.
- Quality control measures may include visual inspection, sampling, and cupping of the beans to assess their freshness, aroma, and flavor characteristics. Buyers compare the received beans to the original samples to ensure consistency and quality standards are met.
- Payment and Settlement:
- Once the quality and condition of the green coffee beans have been verified, buyers proceed with payment and settlement according to the terms of the purchase agreement. This may involve issuing payment to suppliers or producers through wire transfers, letters of credit, or other payment methods specified in the contract.
- Buyers reconcile invoices, receipts, and shipping documents to ensure accurate and timely payment to suppliers. They also maintain records of transactions and financial documentation for auditing and accounting purposes.
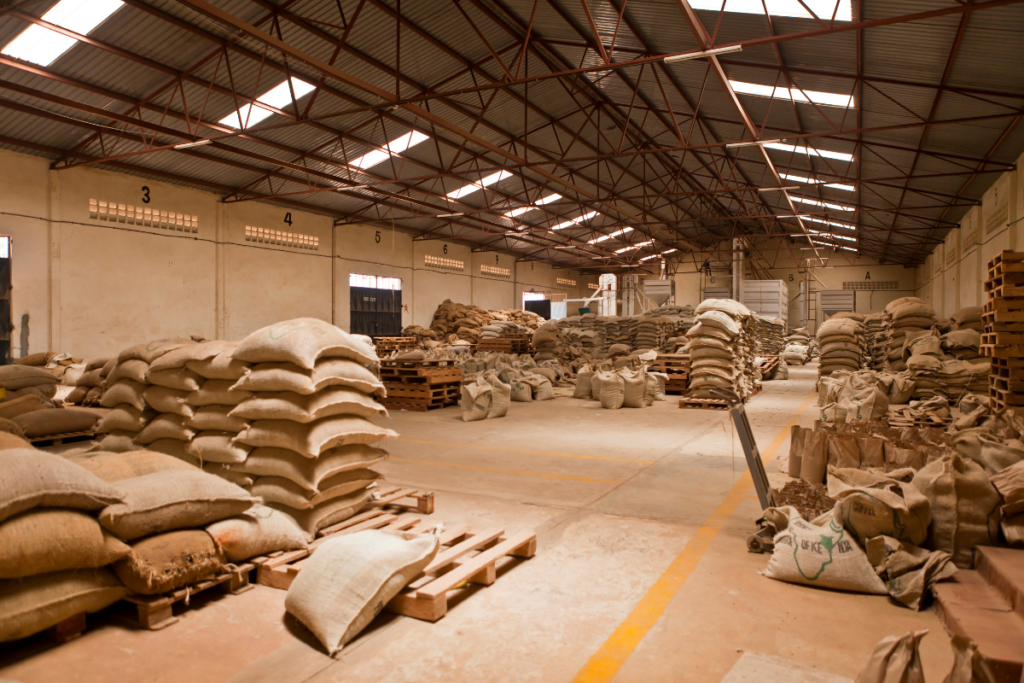
- Storage and Inventory Management:
- After payment is made, buyers take possession of the green coffee beans and arrange for storage and inventory management. The beans are stored in climate-controlled facilities to maintain their quality and freshness until they are ready for roasting.
- Buyers manage inventory levels, rotation, and stock replenishment to ensure a steady supply of green coffee beans for roasting and production. They also monitor market conditions and demand trends to optimize inventory management and procurement strategies.
Overall, the process of evaluating, buying, and receiving green raw coffee requires careful attention to detail, effective communication, and collaboration between buyers and suppliers to ensure the quality, consistency, and reliability of the coffee supply chain. By following established protocols and best practices, buyers can source high-quality green coffee beans that meet their needs and contribute to the success and sustainability of the coffee industry.