El Niño is a climate phenomenon characterized by the periodic warming of sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean, typically occurring every few years. It is part of the larger El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) climate pattern, which influences weather patterns and climate variability around the world.
During an El Niño event, the warming of sea surface temperatures in the Pacific Ocean can have significant impacts on global weather patterns, including:
- Changes in Precipitation Patterns: El Niño can disrupt normal atmospheric circulation patterns, leading to changes in precipitation distribution and intensity. This can result in increased rainfall in some regions and drought conditions in others.
- Temperature Anomalies: El Niño events are often associated with above-average temperatures in certain parts of the world, particularly in regions affected by changes in ocean currents and atmospheric circulation.
- Extreme Weather Events: El Niño can contribute to the occurrence of extreme weather events, such as heavy rainfall, floods, hurricanes, and cyclones, in different parts of the world. These events can have devastating impacts on communities, infrastructure, and agriculture.
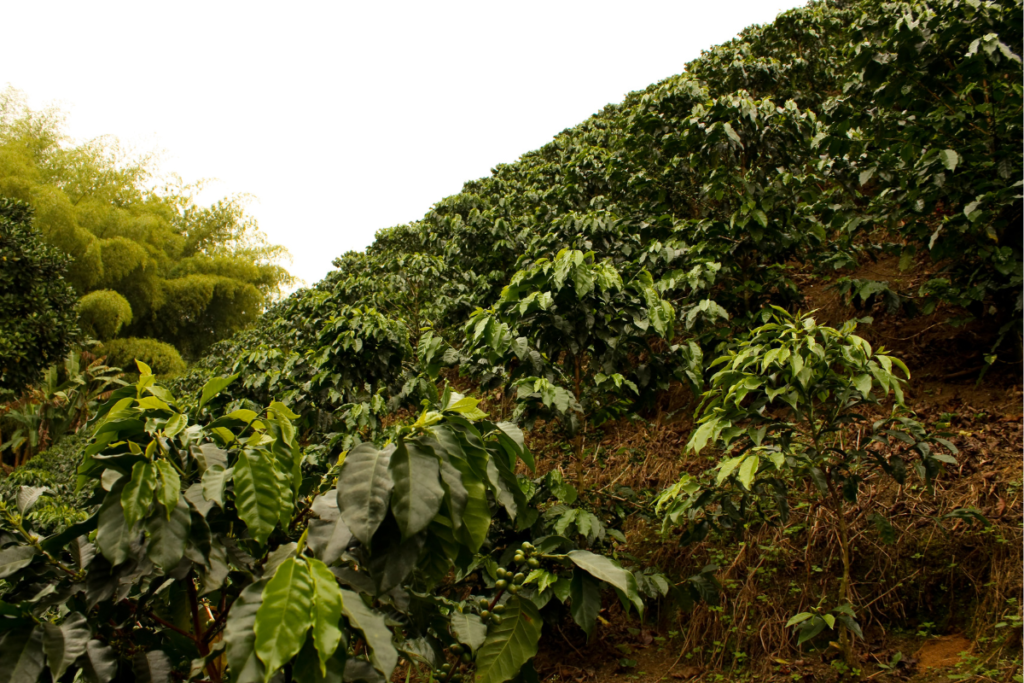
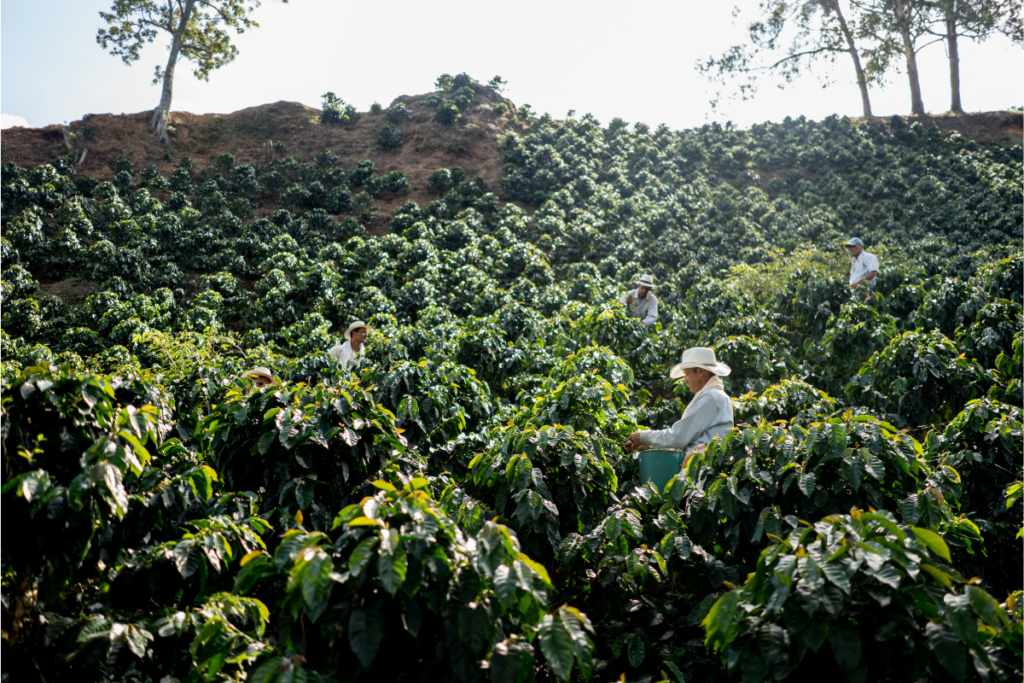
- Shifts in Growing Conditions: The changes in weather patterns associated with El Niño can affect growing conditions for crops, including coffee. In some regions, increased rainfall or warmer temperatures may promote favorable conditions for coffee cultivation, while in others, drought or excessive rainfall can negatively impact coffee production.
The impact of El Niño on coffee production varies depending on the specific region and local climate conditions:
- In some coffee-producing regions, such as parts of Central and South America, El Niño events may bring beneficial rainfall and moderate temperatures, which can enhance coffee tree growth and yield.
- However, in other regions, particularly those already prone to drought or excessive rainfall, El Niño can disrupt coffee production by causing water stress, soil erosion, disease outbreaks, or crop damage.
Overall, El Niño events can contribute to short-term fluctuations in coffee production and quality, posing challenges for coffee growers and impacting global coffee supply and prices. Understanding and monitoring climate patterns like El Niño is crucial for coffee producers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders to mitigate risks and adapt to changing environmental conditions in coffee-growing regions.